Those who are monitoring the developments at IEEE802.3 will not suffer from a lack of ideas about the transfer methods at the moment, as a large number of partly overlapping solutions are currently under development or already standard. Already now it’s foreseeable: not every solution is also a commercial success.
Users seem to have a “wait & see” strategy in this environment, because it would not be possible to explain why optical backbones still work at a 10G level, a technology of the year 2002. Here a new development can be created for aeration – wavelength multiplex via multimode glass fibers. What can be expected from this can be seen in the following article.
Do we have a backlog in optical network investments?
The copper data cable, which is often regarded as limited in its transmission potential, is currently highly popular: not only does it expand the entire building as an IT infrastructure in LAN installations, it simultaneously feeds the WLAN APs, and also links the distributed building technology into the network And, last but not least, is also used for power supply via PoE. Such LANs are now properly designed to 10G (Class EA), which is standardized with 10GBase-T since 2006.
However, the majority of the optical building and sports nets that are required to provide these horizontal structures are also only operated on 10G, which has been standardized with 10GBase-SR since 2002. This is not compatible with the logic of Ethernet LAN, because for a safe operation the backbones should be a “stage” faster than their access networks. That would be according to today’s state of technology 40GBase-SR4, standardized since 2010.
Transceivers for this method are now widely used, in the data center in EOR installations, or backbone consolidation, when four 10G transceivers are replaced by a 40G transceiver, but without increasing the line speed per fiber pair. This is economically meaningful, but technically an on-the-spot.
A hurdle may be the introduction of the 8-multimode fiber-based parallel optics with four parallel-guided 10Gb / s channels. Supporters of the classical 2-fiber topology lead the higher complexity and lack of experience to the long-term behavior of the required MPO connection technology. Also the limited link budget does not make a decision easier. The time is ripe for the 40G deployment, not only because of the network hierarchy, but also because 40G transceivers have now reached a “healthy” price level, which creates the prerequisite for these investments.
We cannot but accepting the limits of our technological possibilities. Today it is not possible to transmit serially 100G and more through a single pair of fibers, this is one source and pone receiver. In practice, we are always dealing with multi-lane methods in which several channels are cascaded. In addition to the variant of multiplying complete transmission paths (laser cable – plug – receiver), there is a solution for parallel routing of the optical channels into one fiber per direction. This so-called WDM (wavelength division multiplex) method has been used for over 15 years in the field of wide-area transmission technology for the requirements at 1550nm. A recent development is the WDM technology with few short wavelengths of 850nm-950nm, also called Shortwave-CWDM or SWDM.
WideBand multimode fibers for SWDM
Today, multimode fibers (MMFs) of the OM3 and OM4 classes are the preferred media for Ethernet and Fiber Channel applications operating at 850 nm with NRZ modulation. If the data rate is to be increased, the effective bandwidth is limited by the modal dispersion of the MMF and the low VCSEL bandwidth. To overcome this limitation, parallel fiber links operating at 10 and 25 Gbps line speed are used to multiply the capacitance. However, this approach requires an infrastructure based on multi-fiber connection technology (MPO). To continue the proven 2-fiber structures is a 100 Gbps solution and moreover, using a single MMF would be preferable. In this context, WDM techniques can be used. For comparison, an OM4-MMF provides a high modal bandwidth, but only a narrow wavelength range centered at 850 nm, limiting its WDM capabilities. The cost-effective operation of at least four WDM channels, each with 25 Gbps, requires high-bandwidth broadband MMFs over an extended wavelength range of 100nm. For backward compatibility, the 850nm wavelength was maintained, resulting in the operating window of 850 to 950nm (see FIG. 1). The performance of MMF in a system is related to the effective bandwidth, which is a function of the effective modal bandwidth (EMB) and chromatic dispersion.
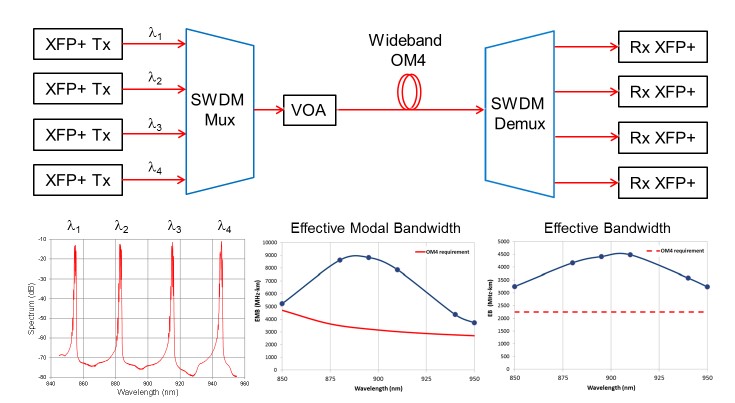
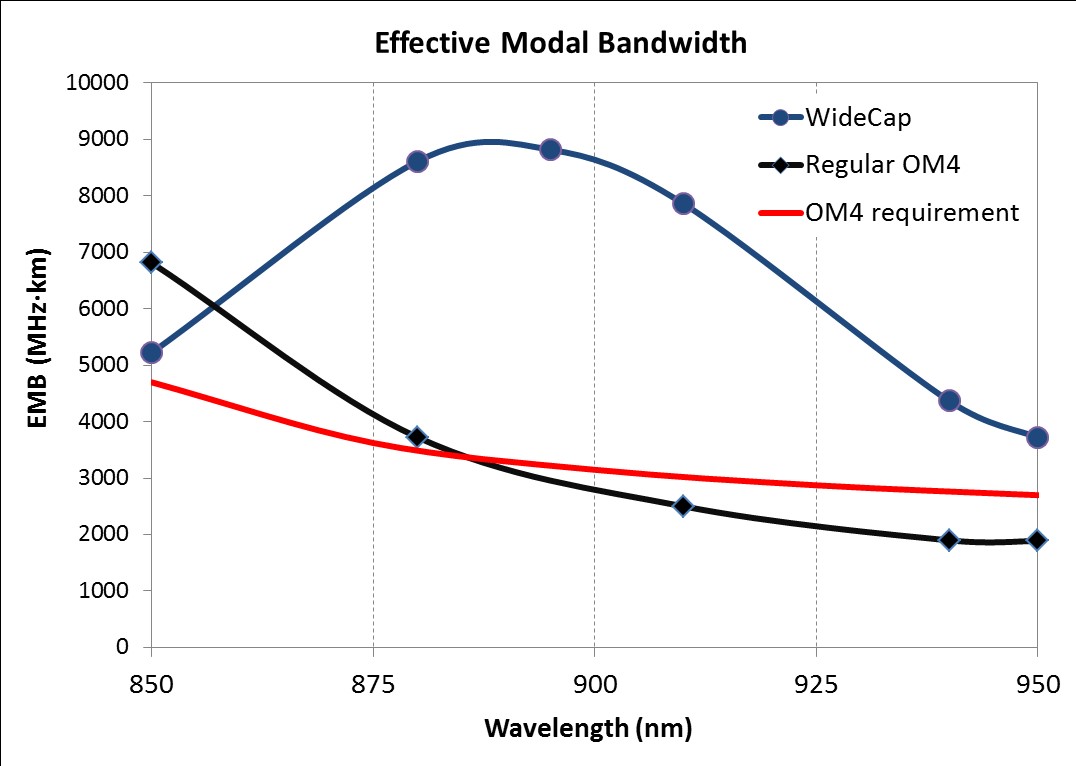
In order to guarantee a constant effective bandwidth of 2,000 MHz * km, the EMB must be 4.700 MHz * km at 850 nm and must not be less than 2.700 MHz * km up to 950 nm (see FIG. 2). WideBand MMFs that meet these specifications are made by optimizing the core profile and tuning the alpha parameter in the GI core glass to shift the peak EMB to 880 nm.
Prototypes of such WideBand MMFs were measured at various wavelengths of 850 to 950 nm using a tunable titanium-sapphire laser. The resulting typical EMB is shown in FIG. 2, as are those of OM4-MMF for comparison. The curves show a peak EMB at 875nm optimized WideBand MMFs, while the standard MMF of the OM4 type has a narrow EMB distribution centered at 850nm. As a result, WideBand MMFs fulfill the EMB specification, while standard OM4-MMF fail at approx. 900nm.
To demonstrate the WDM capability of wide-band MMFs for existing and future system applications, BER tests were performed at 28 Gbps at 850 and 980 nm. The BER evaluation shows the required power reserve after 100m transmission. In addition, the BER was determined using a commercially available 40Gbps duplex transceiver that uses 2 WDM channels, each with 20Gbps at 850 and 900nm. Up to 300m of error-free transmission (BER <10-12) via wide-band MMF is thus possible, which corresponds to the double range of this transceiver. Four WDM channels with 25.8 Gbps from 850 to 950nm with a distance of 30nm and a capacity of 100G reached a distance of 200 m with error-free transmission.
The capacity can be further increased by implementing advanced modulation formats such as PAM-4. In the laboratory, a 180Gbps transmission over a WideBand MMF with four 45Gbps PAM-4 WDM signals was successfully realized, the BER of which had a range of over 300 m, while a maximum of 150 m was achieved with OM4-MMF. These results show the performance data of WideBand MMFs to realize 40, 100 or 200Gbps without the need for parallel fiber optic infrastructures.
Cost comparison
For 40GBase-x, the user now has a choice of options for network operation. Thanks to the standardized QSFP + housing format, depending on the transmission distance, the most cost-effective transceiver variant can be commissioned by plug & play. Currently a well-known pattern is confirmed:
• SM transceivers (40Gbase-LR4) cost between 200% and 400% more than MM transceivers (40GBase-SR4) of the same data rate.
• The price difference of two such transceivers is at least € 600, – and thus the multiple of the cost of the entire passive cabling (a link)
• Thus, an optical fiber backbone based on MMF is the economic solution, if technically feasible.
Some users are concerned that the SWDM technology in the transceiver leads to a lot of additional costs.
A short comparison (Fig. 3) shows that the essential cost elements hold the balance or even more favorable variants.
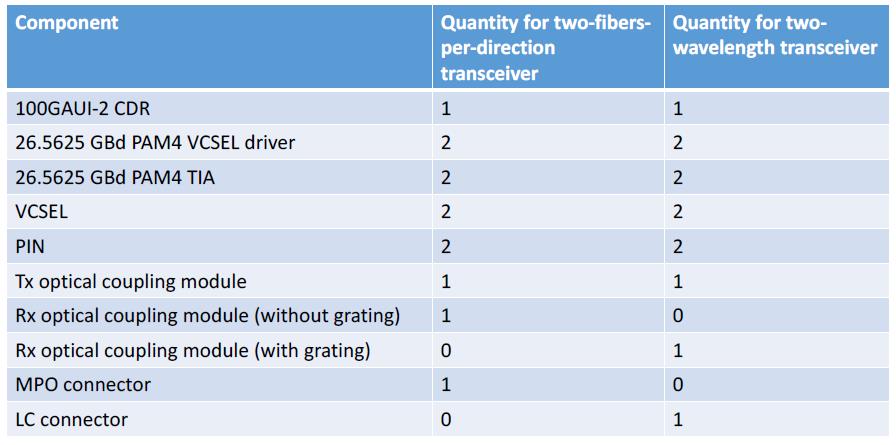
In this context, first commercially available SWDM transceivers are of particular interest. They extend not only the transceiver selection by a further variant, but already allow on the 40G and 100G power level the maintenance of the 2-MMF infrastructure with the proven LC plug.
Conclusion
There are already users whose planning horizon reaches up to 40GbE and beyond. The vast majority of applications are backbone switch-to-switch installations. OM3 with two fibers per line was already present in many cases and a system upgrade often took place step by step. It’s a strong advantage of the described WideBand MMF being fully backwards compatible with all previous MMFs from OM2 to OM3 up to OM4 and not imposing any other requirements to its connecting hardware than the conventional ones. This allows the WideBand MMF to efficiently migrate existing 10G networks to cost efficient 40G and 100G implementations and further up to 200G. At the same time, WideBand-MMF is recognized by IEEE802.3 as Next-Generation MMF and thus supported in case of upcoming network standards.
There is no alternative to MM fibers to those who cannot ignore the costs of LAN and DC network backbones. The new WideBand MMF technology provides a cost-effective transmission technology that is easier to handle due to the LC duplex infrastructure. It is a standardized MM fiber at IEC and TIA, defined as the OM5 cabling class in the forthcoming revision of ISO / IEC11801 and already available with first commercial products.
Credentials:
[1] A. Amezcua, D. Molin, M. Bigot-Astruc, P. Sillard; “Next-Generation Multimode Optical Fibers for Datacom and Telecom Networks”; IEEE Photonics Society Newsletter; Aug 2016
[2] J. Ingham: “Updated baseline for the 100 Gb/s MMF objective using two-wavelength PAM4 transmission”; IEEE P802.3cd; Sep 2016
Authors: Carsten Fehr, Tayfun Eren
Source: Technical MMS UK